Charpy Impact Test vs. Izod Impact Test
Impact resistance is a critical property of materials used in engineering and manufacturing. Structural components must endure sudden forces without catastrophic failure, making impact testing a fundamental procedure in material science. Two of the most commonly used methods for evaluating a material’s toughness are the Charpy impact test and the Izod impact test. While both assess a material’s ability to absorb energy during fracture, they differ in test setup, execution, and practical applications. This article explores the intricacies of each test, highlighting their differences and industrial relevance.
Fundamentals of Impact Testing
Impact testing determines how materials respond to high-rate loading conditions. Unlike tensile or compressive tests, which apply slow and controlled forces, impact tests simulate sudden, dynamic loads that materials may encounter in real-world scenarios. This assessment is particularly vital for brittle materials, which can fail unpredictably under sudden impact.
Several factors influence impact resistance, including material composition, grain structure, heat treatment, and temperature. Temperature, in particular, plays a crucial role—many materials exhibit ductile behavior at high temperatures but become brittle at lower temperatures. Understanding these behaviors allows engineers to select appropriate materials for specific applications, reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
What is the Charpy Impact Test?
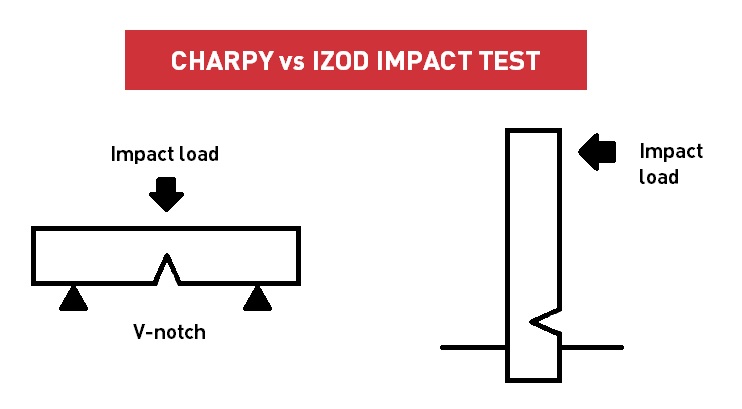
The Charpy impact test is a standardized method used to measure the toughness of a material by evaluating its ability to absorb energy during a sudden impact. It is particularly useful for determining whether a material will behave in a ductile or brittle manner under real-world conditions.
How Does the Charpy Test Work?
- A rectangular notched specimen is placed horizontally on two supports, creating a simple beam structure.
- A pendulum hammer swings down and strikes the specimen at its midpoint, directly opposite the notch.
- The energy absorbed by the material during fracture is calculated based on the difference between the hammer’s initial and final height.
Why is the Charpy Test Important?
- It helps engineers assess the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature, crucial for materials used in cold environments.
- It is widely applied in automotive, aerospace, pipeline, and construction industries to ensure material reliability.
- It is used to evaluate weld quality and material consistency in critical structures.
What is the Izod Impact Test?
The Izod impact test is another common method for evaluating material toughness, often used for plastics, polymers, and composite materials. It differs from the Charpy test mainly in specimen orientation and impact direction.
How Does the Izod Test Work?
- The specimen is positioned vertically, clamped at one end, resembling a cantilever beam.
- A pendulum hammer strikes the free end of the specimen, directly opposite the notch.
- The energy required to fracture the material is calculated from the hammer’s remaining motion after impact.
Why is the Izod Test Important?
- It is particularly useful for testing plastics and non-metallic materials used in consumer products.
- It provides insight into how materials behave under sudden force in real-world applications.
- It is widely used in quality control and product development for impact-resistant materials.
Key Differences Between Charpy and Izod Tests
Despite their similarities in assessing impact toughness, Charpy and Izod tests differ in critical aspects:
| Parameter | Charpy Test | Izod Test |
|---|---|---|
| Specimen position | Horizontal | Vertical |
| Notch orientation | Faces away from hammer | Faces the hammer |
| Impact direction | Three-point bending | Cantilever bending |
| Energy absorption | Measured from pendulum motion loss | Measured from hammer’s final height |
| Common applications | Metals, structural materials | Plastics, polymers, non-metals |
Each test is suited for different materials and conditions, influencing its applicability in various industries.
Factors Affecting Test Results
Several factors influence the accuracy and reliability of impact test results:
- Material Properties: Grain structure, alloying elements, and heat treatment can significantly affect energy absorption.
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature fluctuations alter material behavior—metals transition from ductile to brittle at lower temperatures.
- Specimen Preparation: Notch accuracy and surface finish impact test consistency. Minor variations can lead to significant differences in measured toughness.
Conclusion
The Charpy and Izod impact tests serve as indispensable tools in material evaluation, each offering unique insights into toughness and fracture behavior. While Charpy is favored for metals and structural applications, Izod excels in polymer and plastic testing. Selecting the appropriate test depends on material properties, application requirements, and regulatory standards. As impact testing technology advances, more sophisticated methods will emerge, further enhancing the precision and reliability of material assessment.
STEP Lab provides state-of-the-art testing systems designed for both Charpy and Izod impact tests, ensuring compliance with ISO and ASTM standards. These systems offer high-precision energy absorption measurements, helping industries evaluate material toughness with confidence. Click the button below to discover our impact testing systems.