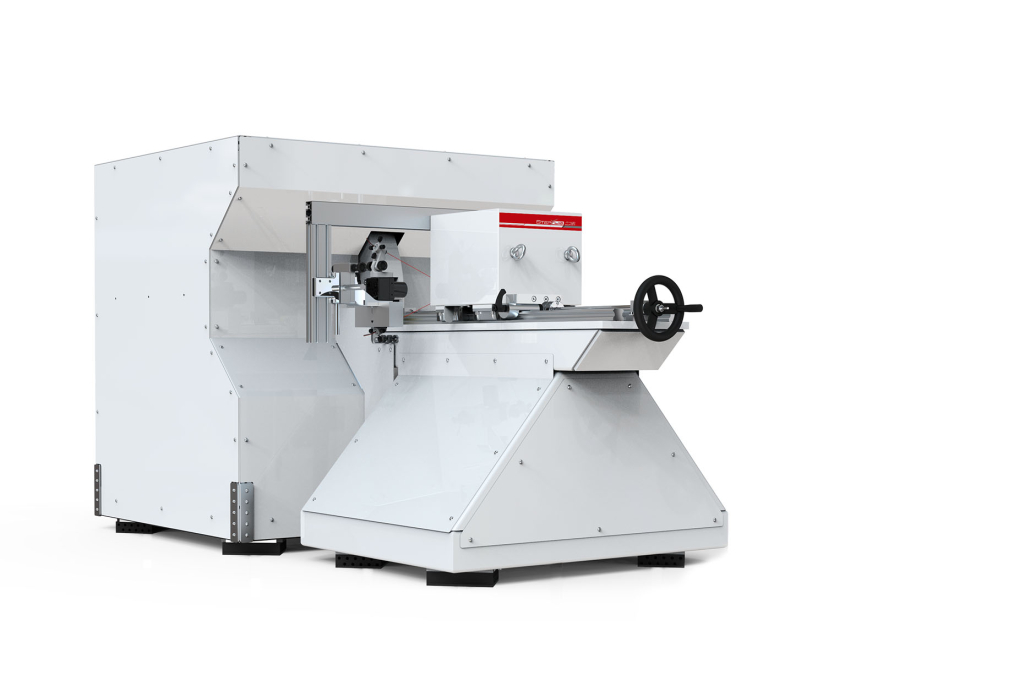
HIGH STRAIN RATE ROTATIONAL SYSTEMS
High-speed dynamic tests are used to replicate car crashes, plane crashes, munitions explosions and other high-impact situations. These tests include both compression and tensile tests, with accelerations up to 40m/s and loads up to 50kN.
Features
Max. Load: 50 kN
Max. Acceleration: 40 m/s
Type of test
High speed
Compression
Tensile
Applications
Plastics
Metal
Composites